Domestic solar thermal
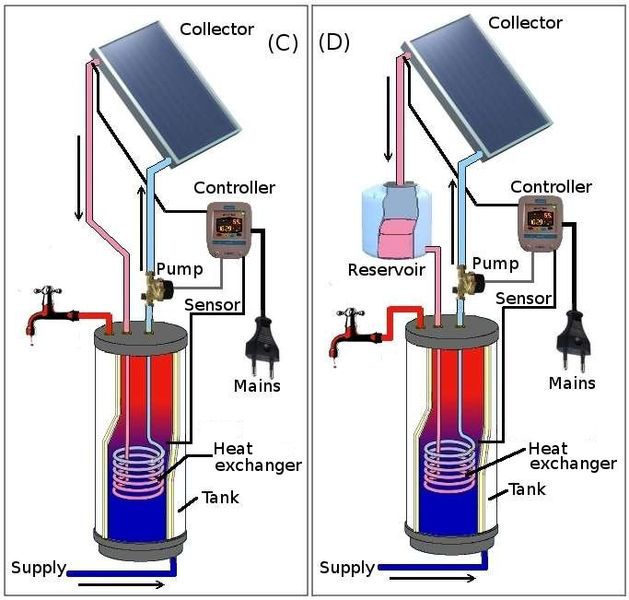
In solar energy systems if the sun’s energy is absorbed and used without mechanical action (pumping or blowing) then this is termed to be a passive thermal system. Passive solar systems rely on gravity and water circulation as it is heated (Demirel 2012). If the solar energy is collected in a fluid or air then moved by pumps and/or fans for use or storage, then this is considered to be an active solar thermal system (Twidell and Weir 2015).
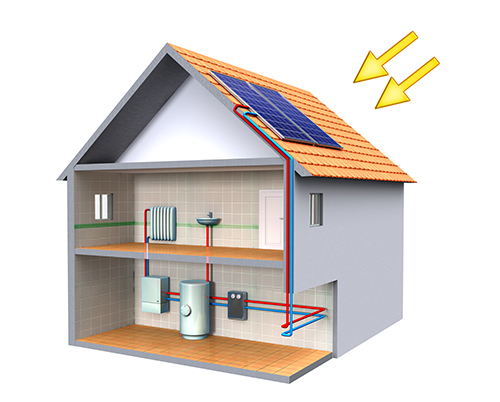
In the domestic context over 200 million households worldwide use solar hot water collectors (Twidell and Weir 2015). A passive solar hot water system is a relatively cheap way of trapping solar energy and storing this energy as heat. It is then used as required for showers, baths, cooking and so on. Installation is a standard plumbing exercise with only an additional heating coil needed in the tank or cylinder (though there may also be an automated control system for the pumps and valves).
In a typical solar hot water system the panel is placed on the roof facing south and can be fitted like a Velux window. There are two types of panel:
- A flat collector is basically a metal plate which captures heat from the sun and transfers this to flowing water;
- A vacuum collector uses glass tubes to convert light to heat (the greenhouse effect) and is therefore effective on overcast days.
However, vacuum collectors (thought to be more effective in Northern latitudes) are more expensive, yet recent field tests show their effectiveness is only on a par with flat collectors (EST 2011). Solar thermal systems are commonly available in a range of sizes from 2m2 to 6m2 collector areas.
It is considered that 60—70% of the hot water in the home can be supplied in the UK from domestic solar thermal installations (EST 2011). These systems will provide most of a household’s hot water requirements between April and September and make a worthwhile contribution in the months either side of this period (YouGen 2013).