Summary
Ultimately, solar PV and solar thermal systems both suffer from a very similar issue to that of wind: intermittency and variability. That said, in certain countries the predictably of cloud-free days is high and so the variability of solar energy is much less than wind power.
The extent of the role of solar power in our future energy mix is also about the cost per kilowatt-hour of solar PV and solar thermal systems. Solar power is considered at present to be the most expensive renewable energy source to produce electricity and is arguably not ready for use on a mass basis (Janardhan and Fesmire 2011). In saying this, the costs are reducing annually as the lifespan of PV panels improves, the efficiency improves and the production costs reduce. According to MacKay (2009) a commercially available PV solar panel with 30% efficiency will be a quite remarkable outcome.
As Patterson (2007) points out the costs of solar power may seem higher than much fossil fuel generation, but the full costs of fossil fuels to the environment are not being included in their price and so in this context solar power is a much more competitive technology. Solar energy is a benign technology often unobtrusive and built into roof designs, its operations give off no harmful emissions and the manufacture of solar panels involves no dangerous materials or techniques. With only minimal servicing, installations are expected to have a working life of 25-35 years (Twidell and Weir 2015).
A 4m2 solar thermal collector is able to produce all the hot water required for a family of 4 in the UK between April and September (ibid). The price reduction in solar photovoltaics from $40/W in the 1980s to $1/W in 2013 has mirrored the growth in this technology worldwide. In countries which have introduced market mechanisms (e.g. the feed-in tariff) such as Germany and the UK to reduce carbon emissions, photovoltaic production and installations have increased the most. According to Twidell and Weir (2015) it is not unreasonable to speculate that solar PV within two decades will be incorporated into the standard roof structures of all new build housing and will become the norm on rooftops across much of the developed and developing worlds.
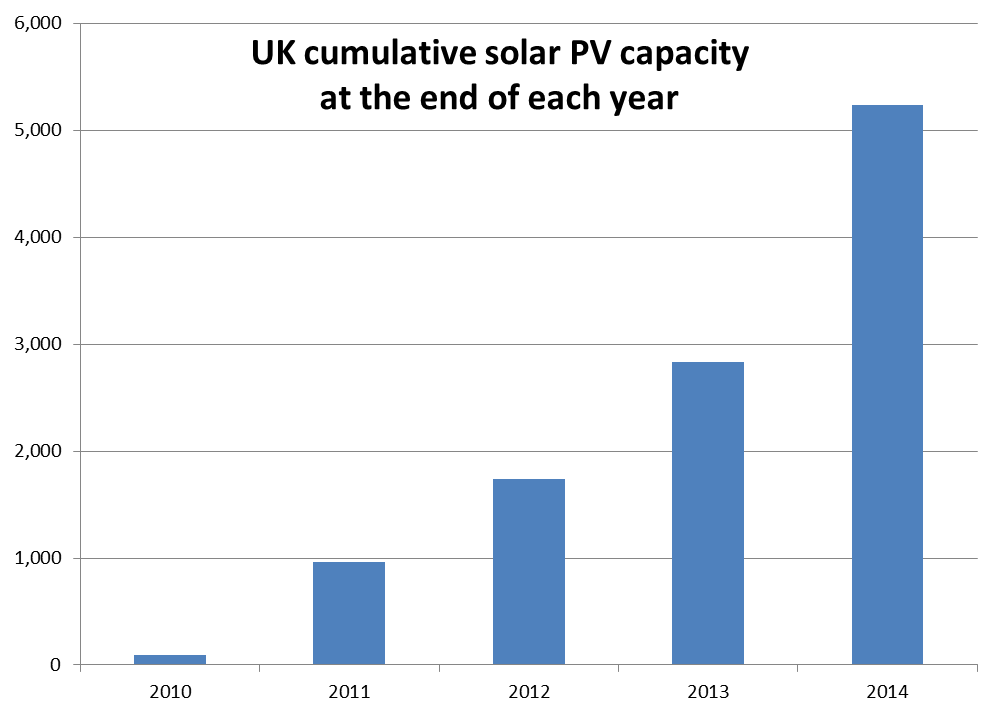
Data from Gov.uk