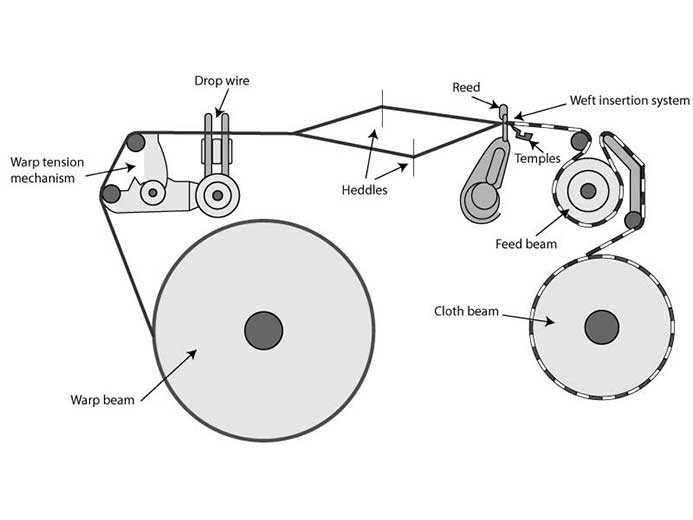
Weaving process
Weaving is the interlacing of warp and weft strands to create fabric. The weaving machine (loom) provides the mechanisms needed to deliver and control warp threads for interlacing weft yarns.
Warp beam: Leading the warp for weaving process
Warp tension mechanism: The warp yarns are led from a warp beam over a beam that controls the warp tension
Drop wire: The warp threads pass through drop wires which stop the machines in the case of any warp breakage. Then a reed moving forward and backward beats the weft (filling) yarn into position and the process is repeated.
Heddles: The heddles raise or lower warp in order to make a shed.
Reed: The reed moved forward and backward to beat the weft (filling) yarn into position and the process is repeated.
Weft insertion system: Weft yarns are inserted using a weft insertion device to transport the weft yarn from one side to the other.
Temples: Temples are placed on both sides in order to control the fabric width and make sure the warp strands do not break in the selvage.
Feed beam: This beam transports the fabric through the loom.
Cloth beam: The fabric is taken-up by the cloth beam.