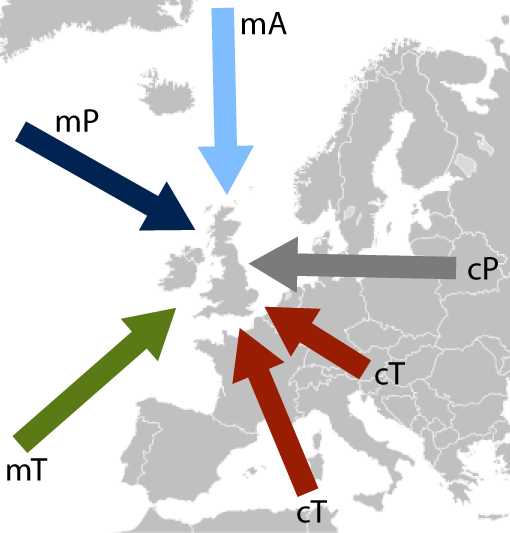
Air mass types and seasonality
Some air masses are seasonally dependent. For example, in Europe, the Continental Polar (cP) air mass occurs only during the winter half of the year – as the Eurasian continent heats up considerably during the summer. Likewise, a Continental Tropical (cT) air mass may develop over both the European and North African landmasses during summer, but arrives only very rarely from North Africa in the winter. A summary of five of the principal air mass types that affect the British Isles is given in the following Table:
| Air Mass Name | Abbr. | Origin of Air Mass | Winter conditions | Summer conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maritime Tropical | mT | Between Bermuda and the Azores in the North Atlantic Ocean | Dull, windy, mild, rain | Dull, rain in west, warm on leeward slopes |
| Maritime Polar | mP | Between the Davis Strait, Labrador and Greenland (but modified considerably after passing over Atlantic) | Cold, windy, showery | Cool, blustery, showery. Bright in-between showers. |
| Maritime Arctic | mA | Between Iceland, Svalbard and Norway | Crisp, wintry showers, frost at night | Cool, bright, heavy showers |
| Continental Polar | cP | Eastern Europe, Russia and rarely Siberia (but modified after passage over the North Sea). | Bitterly cold, snow showers on east-facing coasts and slopes | Doesn’t occur in summer |
| Continental Tropical | cT | North Africa and the European continent | Rarely occurs in winter (only from North Africa) | Warm, mostly sunny, possible heat-wave |
Table 1: Five of the principal air mass types that affect the British Isles during the year (after Belasco, 1952). The name, abbreviation, origin of air mass and typical summer and winter conditions (for the British Isles) are given.
The recurring weather types that affect the British Isles can also be described in terms of the direction of origin of the air mass. Thus, a Maritime Tropical (mT) air mass can also be described as “south-westerly” and a Maritime Polar (mP) air mass as “westerly” or “northwesterly”. This type of air mass classification is known as a “Lamb Circulation Type” or “Lamb Airflow Type”, after the famous 20th century climatologist Hubert Lamb (Lamb, 1950). The use of Lamb air circulation types enables classification of weather conditions during slow-moving or self-generating air mass conditions, as sometimes happens during “Cyclonic” or “Anticyclonic” weather conditions.