WWW: World Wide Web → The Web
- Provides access to information, to linked resources distributed at many hosts
- Allows:
- Receive (and publish) information
- “Navigate through an ocean” of information via hyperlinks, and the interaction of different Web pages
- Operates:
- On demand
- Users receive and publish “what they want” “when they want”
- Client-Service Model
- On demand
- Elements of the web architecture
- Pages
- HTML, hypertext, hyperlinks
- Objects
- Can reside at the same or another host
- Addressing
- URL: Uniform Resource Locator
- Functional Entities
- Web Client (Navigator)
- Web server
- HTTP Protocol
- Pages
- Addressing
- With a URL: Universal Resource Locator
- Element for addressing resources
- URL parameters
- Service identifier (protocol)
- Domain name of Server Host
- Path to access object
- Object name
- URL syntax
- Characters “://” separate first parameter from second one
- Character “/” used to separate the rest of parameters
- With a URL: Universal Resource Locator
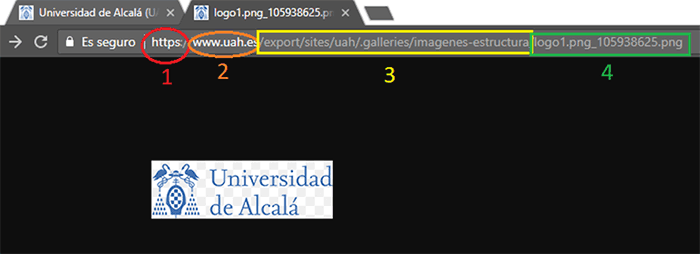
Figure 10 Example of URL showing the four types of parameters that usually compose it
- Web Client (Browser)
- Includes:
- User agent
- Software that provides an interface between the user and Web application
- Captures and visualizes pages and allows navigation through their contents
- Diverse configuration characteristics
- HTTP Client
- Communication software that implements the HTTP Client part
- Best known browsers:
- Chrome
- MS Internet Explorer / Edge
- Firefox
- User agent
- Includes:





