Animal fibres
-
Introduction
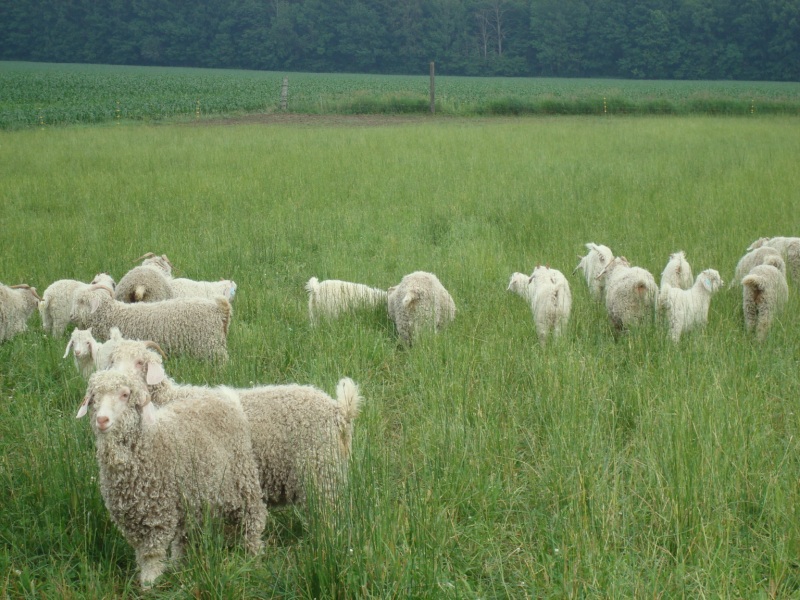
Wool fibres
Animal fibres consist largely of particular proteins.
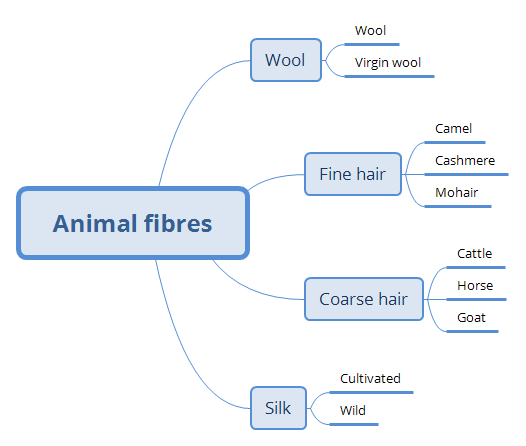
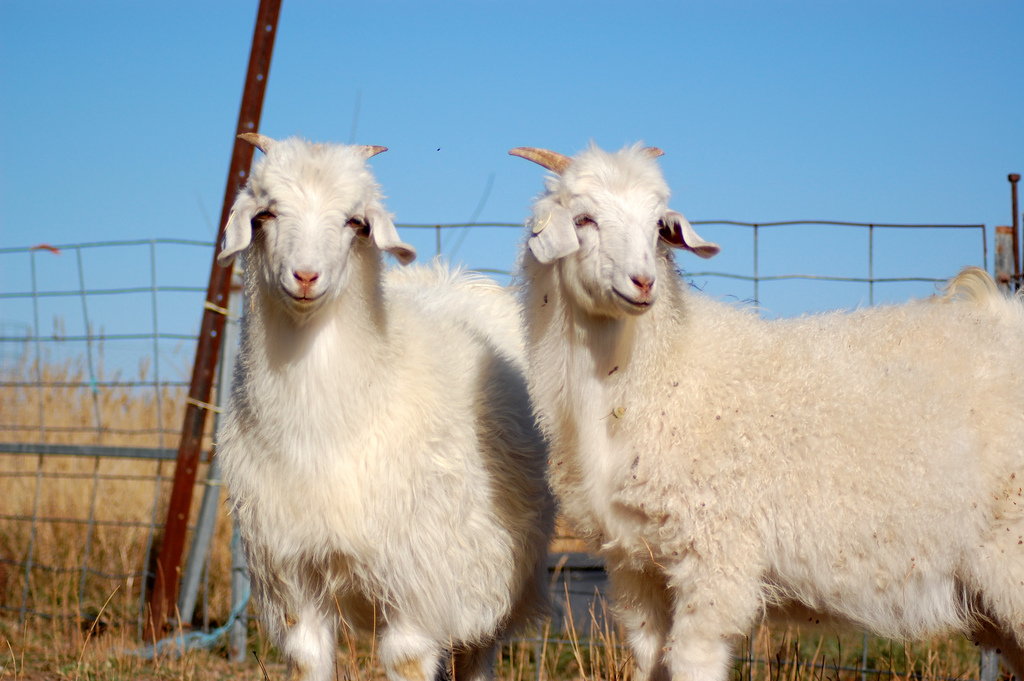
Animal based fibres
Silk fibreWool fibres
- Major hair fibre
- 5% of Fibre market
- Origin: Australia, New Zeeland, China, Eastern Europe, turkey, UK, Argentina, Uruguay, South Africa, USA
- Merino 90% of all Sheep wool
The structure of wool fibres
The wool fibre is made of keratin (protein molecules). The long chain protein molecules are formed into fibrils.
Wool production
Click on the headings below for more information
Classing
1 = best, 4 = worst. The grader classifies the wool according to: finess, crimp, length, impurities and colour
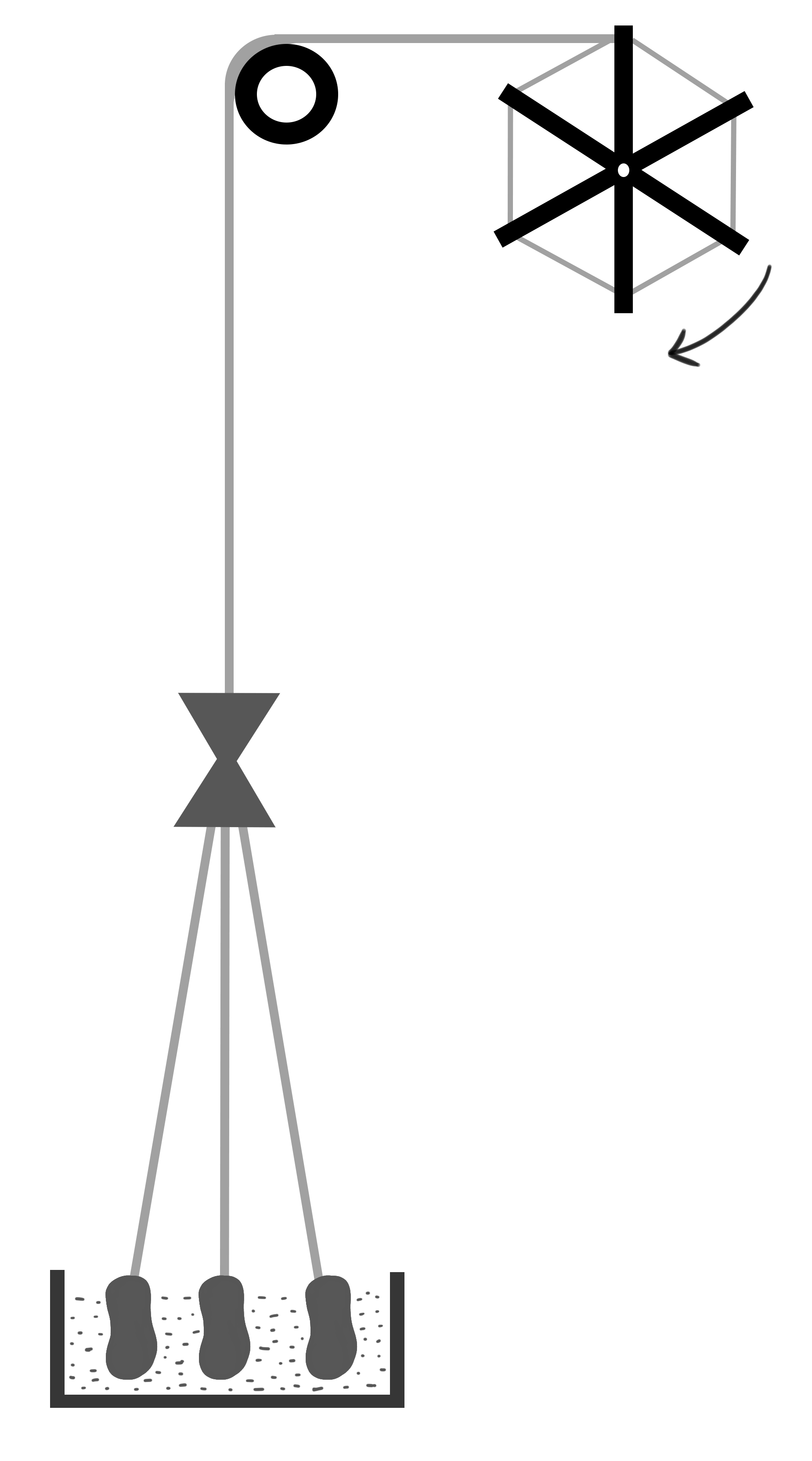
×Scouring
- Remove nonwool containers such as dirt and most of the grease (lanolin)
- 40% of weight is removed
- Washing in hot water and detergent
Carbonising
- Removes burrs and other vegetables
- Acid impregnation
- Sulfuric acid (svavelsyra) degrades cellulosic impurities
- Baking in order to excess acid
- Mechanical rollers to crush residues
- Neutralisation and rinsing of acid
Processing
Wool fibre spun into yarn by Worsted or Woolen process:
- Worsted
- Fine Smooth Yarn
- Long staple fibres
- Gilling: parallelising fibres
- Combing: Comb fibres to remove short fibres
- Woolen
- Coarser more bulky yarn
- Spun from shorter fibres
- No combing
© University of the Highlands and Islands
Goat fibres- Origin: China, India, Uzbekistan, Brazil, Iran, Thailand, Vietnam, Korea, Romania
- Larva of silkworm
- Cultivated silk (Mulberry): The best-known silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larva of the mulberry silkworm.
- Wild silk fibre: Beside the mulberry silkworm, there are many wild spices. Wild silk comes from insects that live in wild or semi-domesticated conditions.
- Tussah Silk, Coarser, stronger, Different colours
- Heavier than cultivated silk, Not so uniform, Cheaper
Processing
Egg
Caterpillar – Mulberry leaves
Chrysalis – Cocoons
Chrysalis is killed with steam or dry heat
Cocoons are grades and sorted
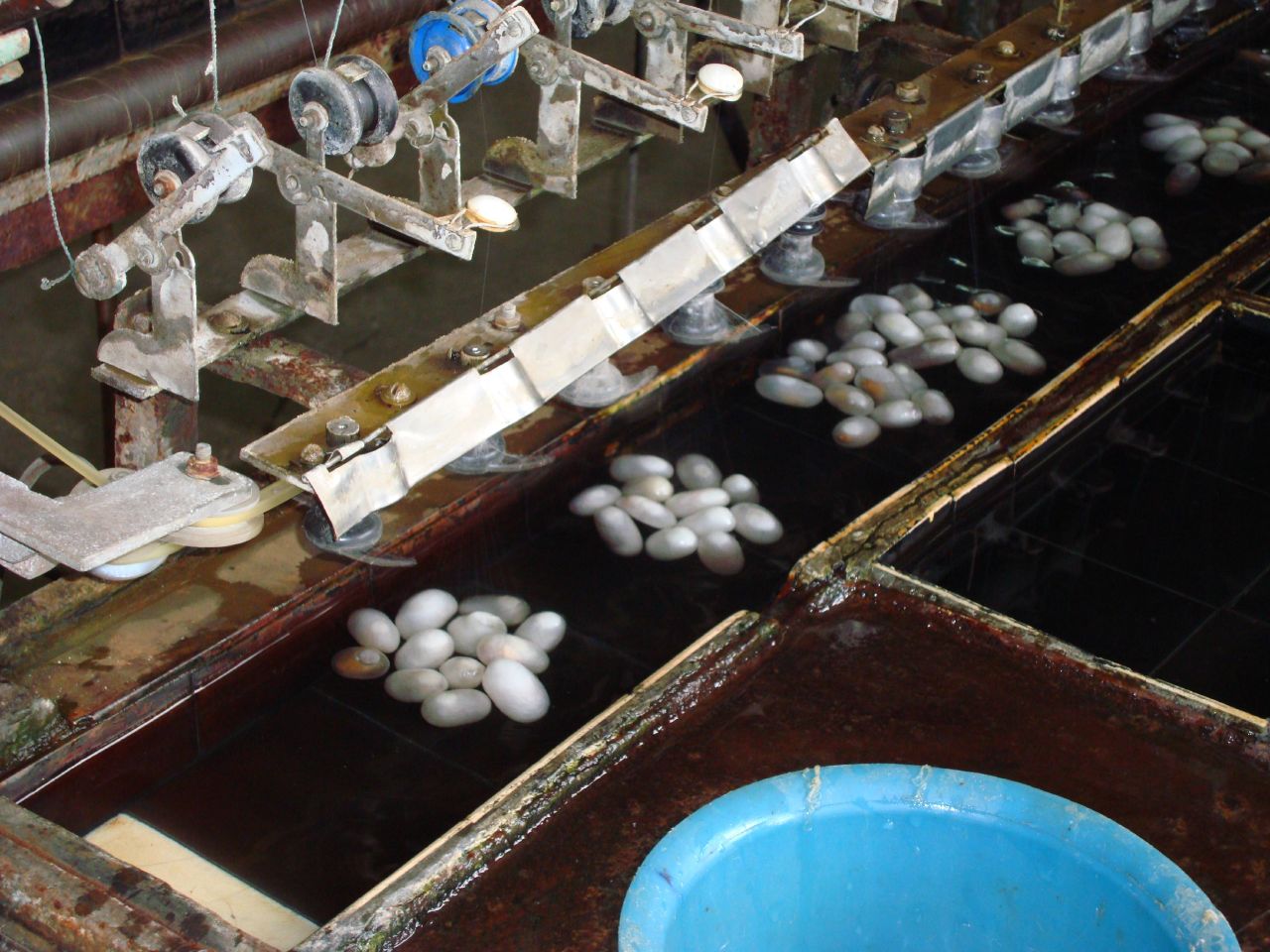
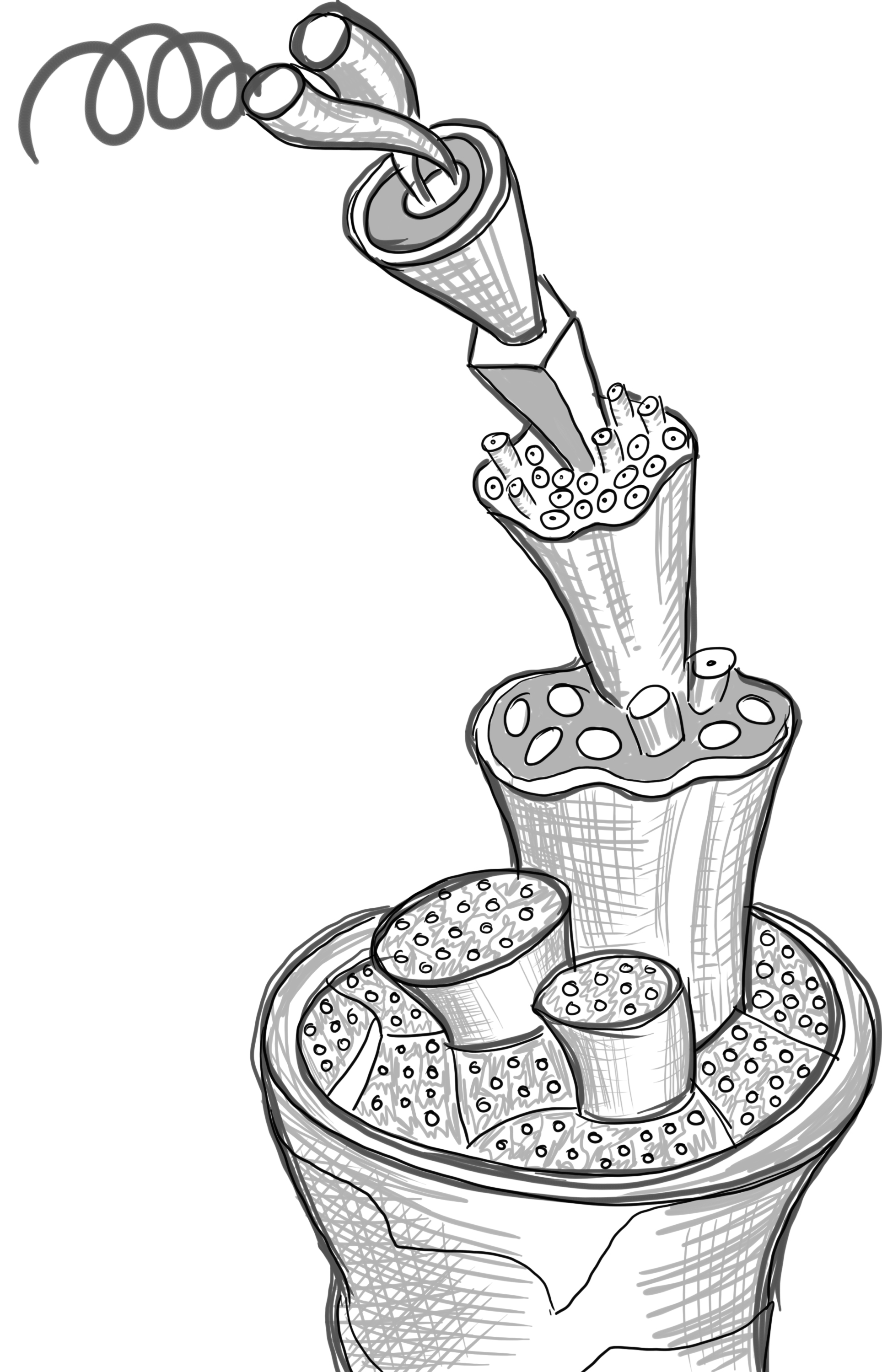
Silk reeling
The cocoons are placed in hot water to soften the gum and then the filaments wound up onto a reel (opposite).
Improvement of properties by finishing
- Degumming:
- Boiling of yarn/fabric in soap solution
- Finer fibres – double no of fibres
- Weight reduction 20-30%
- Weighted Silk:
- Lead and tin
- More rigid
- Sustainability, elasticity and resistance to light is reduces
Silk reeling
© University of the Highlands and Islands
-
Project
Contact
This resource was developed as part of an Erasmus+ project, funded with support from the European Commission under grant agreement 2016-1-SE01-KA203-22064.
The project was a collaboration between:
- The University of Borås, Sweden
- The University of the Highlands and Islands, Scotland
- The University of Alcalá, Spain
- Digital Connections, Scotland
This resource has been released under Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 4.0.
Disclaimer
If you would like more information on this resource please contact:
- Academic content – The University of Boras (www.hb.se)
- Technical resource development – The University of the Highlands and Islands Educational Development Unit - EDU (edu@uhi.ac.uk)
Except where otherwise noted, this website is licensed under Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 4.0. All images used under permission remain the copyright of the license holder.
Download a copy of this resource in PDF format.
You can also print individual pages by printing directly from the browser.
-









