Printing
Printing can be described as localised dyeing in different patterns on a substrate.
There are several basic approaches to print colour on a fabric. Click on each item below for more information:
-
Direct printing
Applying the printing paste directly to the fabric surface with desired pattern.
Direct printing on fabric (YouTube, 3:40)
-
Discharge printing
Overprinting a plain dyed fabric with a discharge paste which changes or destroys the colour in the designed areas
Discharge printing (YouTube, 2:07)
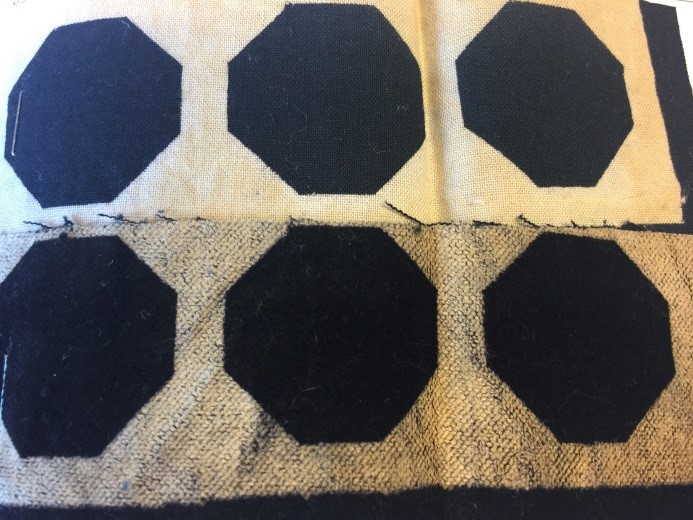

Printing with discharge print paste
© University of Borås -
Resist printing
Printing with a resist paste and passing the fabric through a subsequent dyeing process (the printed area is not coloured).
Resist printing (YouTube, 1:38)
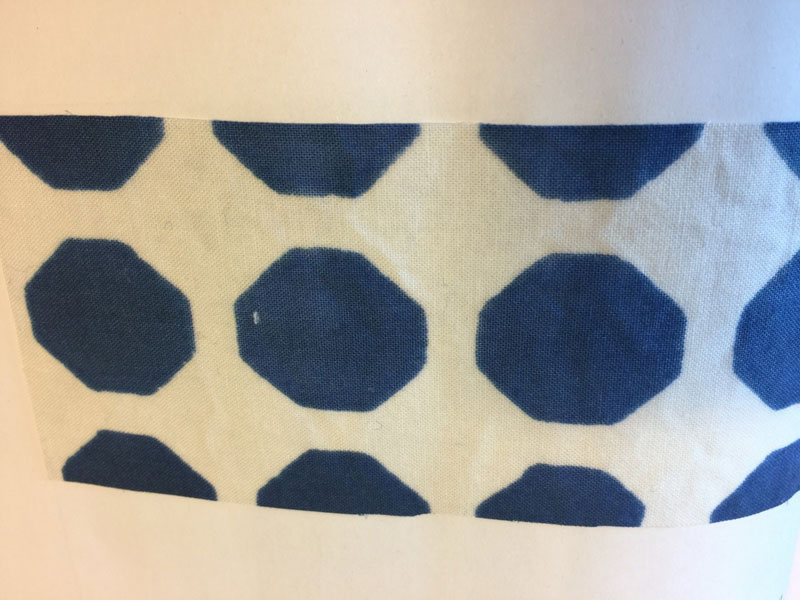

Resist print
© University of Borås -
Transfer printing
Literally moving a design from one surface to another. Printing the design on to a special type of paper and transferring the pattern to the fabric with the help of a heated calendar.
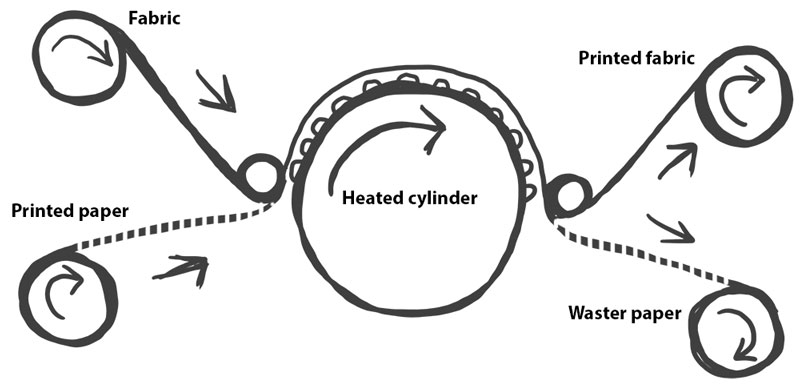
Heat transfer printing
© University of Borås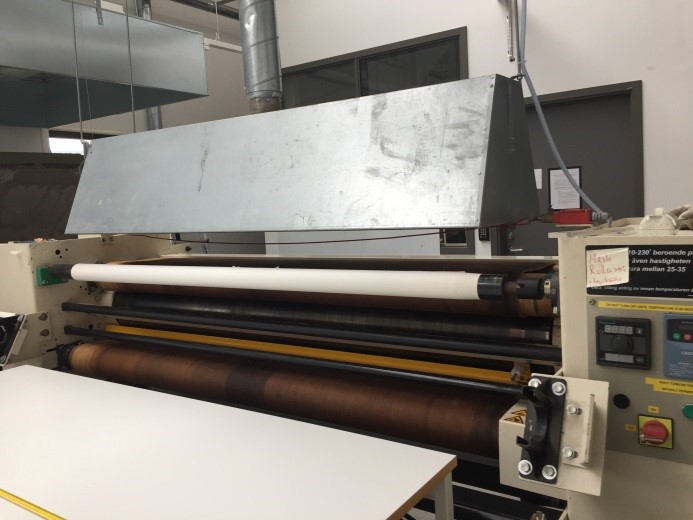
Heat transfer printing
© University of Borås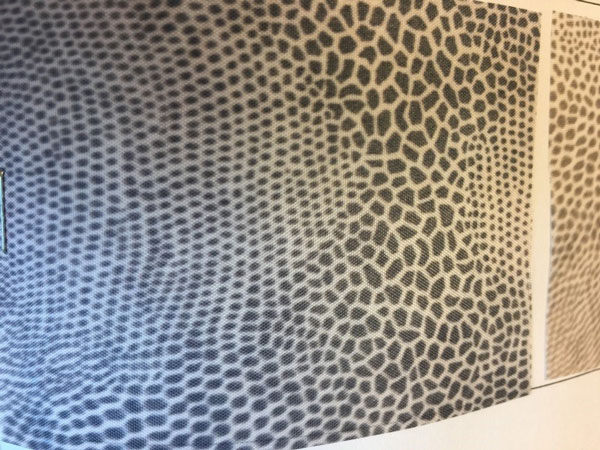
Transfer printing
© University of Borås -
Flock printing
Flock printing or flocking is a printing process in which glue is printed on the fabric and then the fibre flock is applied on the adhesive-coated surface.
Flock printing (YouTube, 2:31)
Flock printing
© University of Borås -
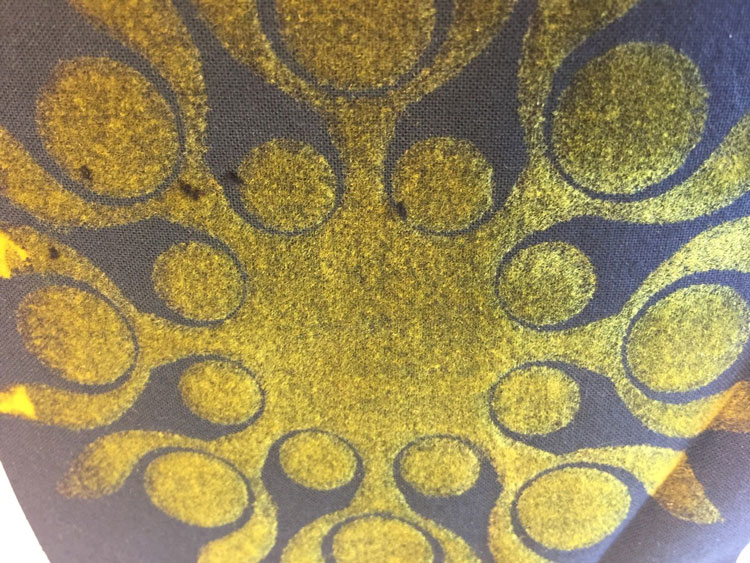
Pigment printing
Pigments are colour that are insoluble and do no penetrate into the fibres. Embedding the pigment colour with a film-forming binder.
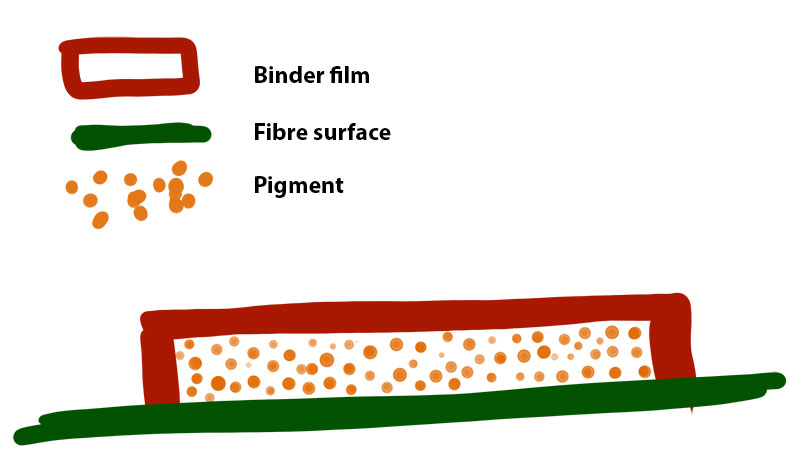
Pigment printing
© University of Borås -
Warp printing
Printing the pattern onto the warp sheet before weaving.
Warp printing
© University of Borås -
Roller printing
The oldest mechanised method of continuous printing. Printing the fabric with engraved metal roller with the printing design. One roller per colour in printing design
Roller printing (YouTube, 5:07)
-
Hand printing
The oldest method of printing. Applying the printing paste by means of a wooden block or by a stencil.
Block printing (YouTube, 5:29)
-
Screen printing
The most important printing method. Forming the design on a screen by blocking off those parts of the screen where no printing is to happen. Coating the screen with light-sensitive polymer and then selectively exposing through a stencil. Washing away the unexposed area (Exposed areas are made insoluble.)
Flat screen printing
- Holding the fabric firm and flat on a conveyor blanket.
- Supplying printing paste to the screens and forcing through the patterned areas by a squeegee roller or blade.
Flat bed screen printing (YouTube, 2:12)
Rotary screen printing
- Continuous production.
- Pumping the printing paste from the reservoirs to the inside of the cylindrical screens.
Rotary screen printing (YouTube, 4:56)
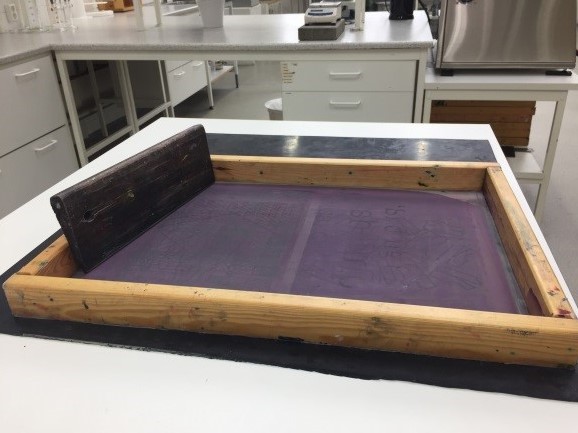

Flat screen printing
© University of Borås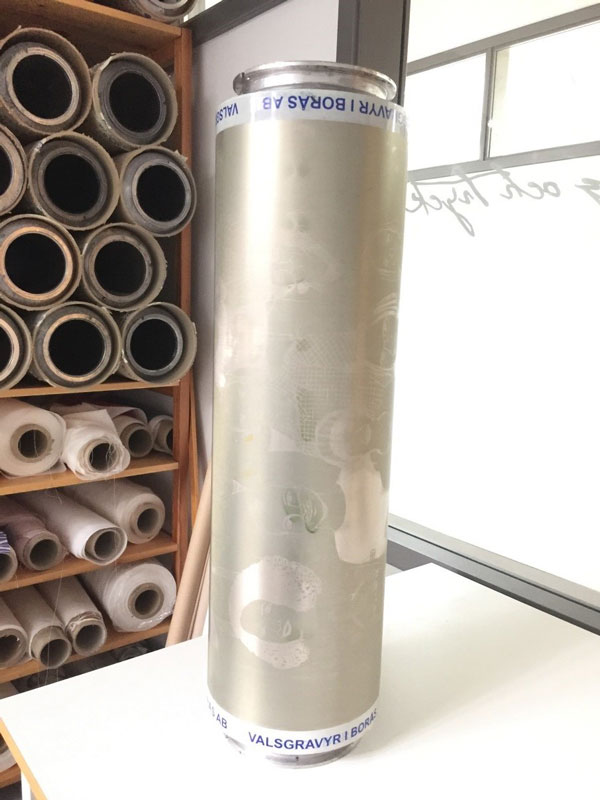
Rotary screen printing
© University of Borås
-
Project
Contact
This resource was developed as part of an Erasmus+ project, funded with support from the European Commission under grant agreement 2016-1-SE01-KA203-22064.
The project was a collaboration between:
- The University of Borås, Sweden
- The University of the Highlands and Islands, Scotland
- The University of Alcalá, Spain
- Digital Connections, Scotland
This resource has been released under Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 4.0.
Disclaimer
If you would like more information on this resource please contact:
- Academic content – The University of Boras (www.hb.se)
- Technical resource development – The University of the Highlands and Islands Educational Development Unit - EDU (edu@uhi.ac.uk)
Except where otherwise noted, this website is licensed under Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 4.0. All images used under permission remain the copyright of the license holder.
Download a copy of this resource in PDF format.
You can also print individual pages by printing directly from the browser.
-





