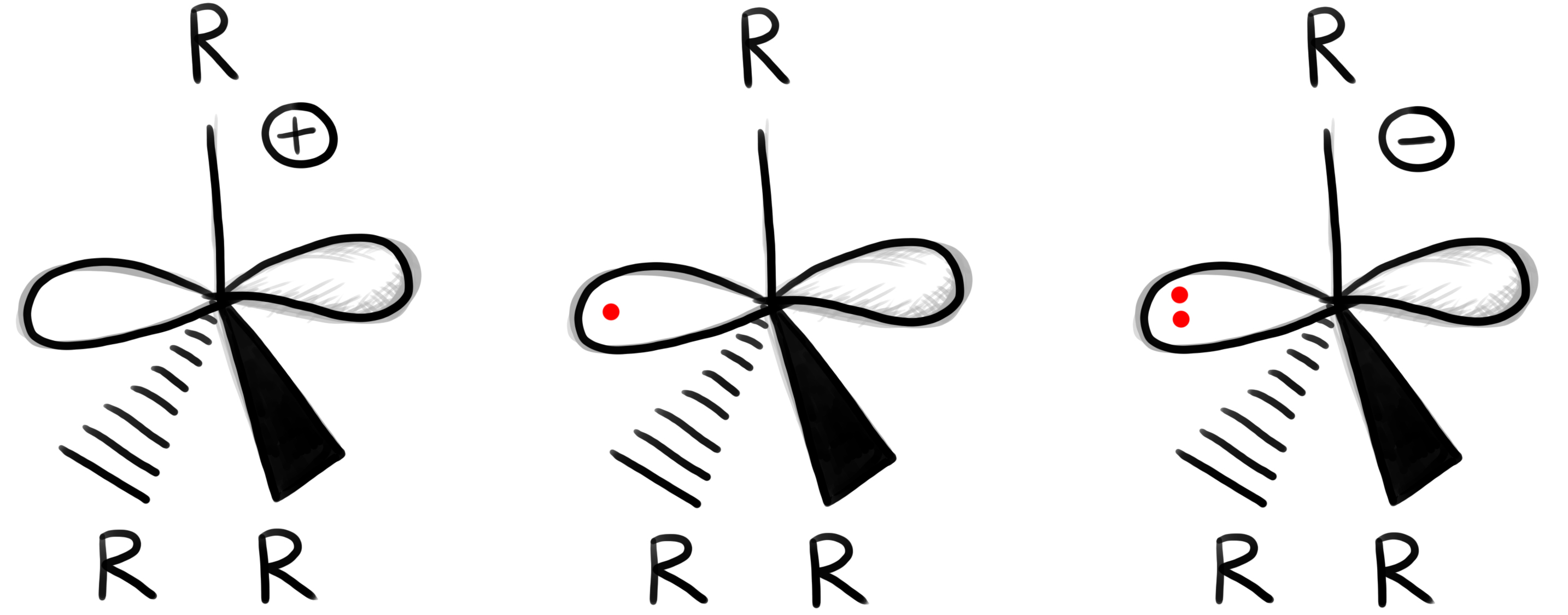
Reaction intermediates
Carbocation: An organic molecule with a positive charge on a carbon atom.
- The carbon atom has only 6 electrons in its valence shell.
- The carbocation is formed by heterolytic bond cleavage.
Carbanion: Has a free pair of electrons on a carbon atom that already has three bonds.
Radicals: Molecule with one or more unpaired electrons (an orbital with only one electron – high energy)
Formed e.g. through oxidation, reduction or by homolytic bond cleavage.
© University of the Highlands & Islands
-
Project
This resource was developed as part of an Erasmus+ project, funded with support from the European Commission under grant agreement 2016-1-SE01-KA203-22064.
The project was a collaboration between:
This resource has been released under Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 4.0.
Contact
If you would like more information on this resource please contact:
- Academic content – The University of Boras (www.hb.se)
- Technical resource development – The University of the Highlands and Islands Educational Development Unit - EDU (edu@uhi.ac.uk)
Disclaimer
Except where otherwise noted, this website is licensed under Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 4.0. All images used under permission remain the copyright of the license holder.
PDF
Download a copy of this resource in PDF format.
You can also print individual pages by printing directly from the browser.
×






