Operational security: Firewalls
Isolates organization’s internal net from larger Internet, allowing some packets to pass, blocking others:
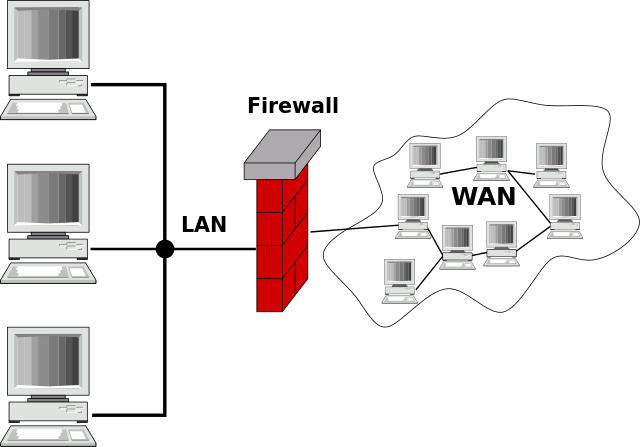
Figure 39 The firewall filters the flow of packets between the LAN and WAN
Gateway Firewall... by Harald Mühlböck... from Wikipedia CC BY-SA 3.0
Prevent denial of service attacks:
- SYN flooding: attacker establishes many bogus TCP connections, no resources left for “real” connections
Prevent illegal modification/access of internal data
- e.g., attacker replaces CIA’s homepage with something else
Allow only authorized access to inside network - Set of authenticated users/hosts
There are three types of firewalls:
- Stateless packet filters: decision to forward/drop packet based on source, destination IP address, TCP/UDP source and destination port numbers, ICMP message type and TCP SYN and ACK bits.
- Stateful packet filters: tracks status of every TCP connection to drop packets that “make no sense”. Basically, track connection setup (SYN), teardown (FIN).
- Application gateways: Filter packets on application data as well as on IP/TCP/UDP fields.





