Internet network layer
The main function of the network layer is to forward packets from an origin to a destination.
- The IP protocol implements addressing conventions, datagram format and packet handling conventions
- The routing protocols configure the routers’ forwarding tables to perform efficient path selection
- RIP, OSPF and BGP are the facto routing protocols in the Internet
The IPv4 (IP version 4) datagram has the following format:
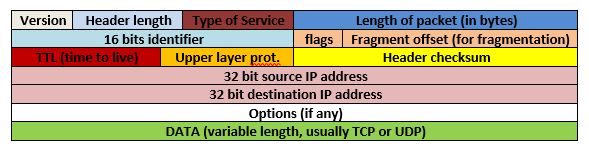
Figure 7 IPv4 Datagram format
Usually, an IP packet has a 20 bytes header without options. Header Length is the number of 32 bits header words. Type of Service can be used to define the “type” of data. Every IP packet has a 16 bits identifier. Flags and Fragment offset are used in IP fragmentation. Fragmentation occurs when IP packets are bigger than the Maximum Transfer Unit (MTU) of a link. TTL determines the maximum number of hops permitted to the packet. The Upper layer protocol specifies the protocol used in the DATA field. Next we have the header checksum and the 32 bits source and destination addresses.





