Link-state routing algorithm
Dijkstra’s algorithm:
- Needs the net topology and link costs known to all nodes
- Accomplished via “link state broadcast”
- All nodes have same info
- Computes least cost paths from one node (‘source”) to all other nodes
- Gives forwarding table for that node
- It is iterative: after k iterations, know least cost path to k destination
Notation:
c(x,y): link cost from node x to y; = ∞ if not direct neighbours
D(v): current value of cost of path from source to dest. v
p(v): predecessor node along path from source to v
N': set of nodes whose least cost path definitively known
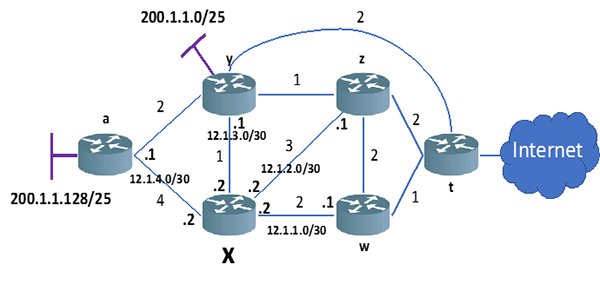
Figure 13 Example of IP network with link costs
The table below shows the resulting shortest-paths from X after the execution of the Dijsktra algorithm in router X:
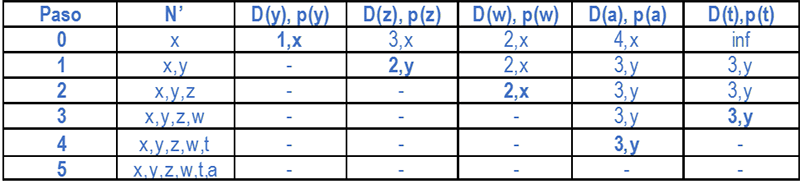
Figure 14 Computation of shortest paths using the Dijsktra algorithm
Once we have the shortest paths and the previous nodes to follow those paths, it is straightforward to obtain the spanning tree and then the forwarding table:
Spanning tree
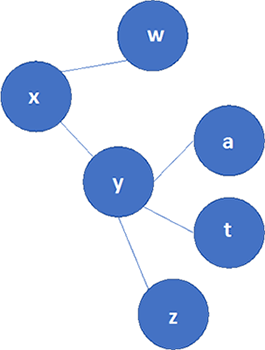
Figure 15 Spanning tree resulting from the execution of the Dijsktra algorithm in node X
Forwarding table
| Destination | Next Hop |
| W | W |
| Y | Y |
| Z | Y |
| A | Y |
| T | Y |
Figure 16 Simplified forwarding table in router X
Figure 16 shows a forwarding table. It can be easily obtained from the spanning tree by looking at the root node X and then the adjacent nodes. The first column shows all the destinations. The second column defines the next hop (adjacent node) to reach the corresponding destination.This figure shows a forwarding table. It can be easily obtained from the spanning tree by looking at the root node X and then the adjacent nodes. The first column shows all the destinations. The second column defines the next hop (adjacent node) to reach the corresponding destination.
Routing table
Destination |
Gateway (Next-hop) |
Interface |
Default |
12.1.3.1 |
12.1.3.2 |
Figure 17 Resulting routing table in router X
Figure 17 shows a routing table. The first column represents the IP and network mask, i.e. the destination network. The second column shows the gateway or next-hop IP. This is the IP of the router where the packet must be sent to reach a destination. The last column is the interface which defines the outgoing port of the router where it must send the packet.





