IEEE 802.11: CSMA/CA
802.11 sender:
- If sense channel idle for a time DIFS, then transmit entire frame (no CD)
- If sense channel busy then start random backoff time timer counts down while channel idle transmit when timer expires. If no ACK, increase random backoff interval, repeat 2
802.11 receiver:
- If frame received OK return ACK after a period of time SIFS (ACK needed due to hidden terminal problem)
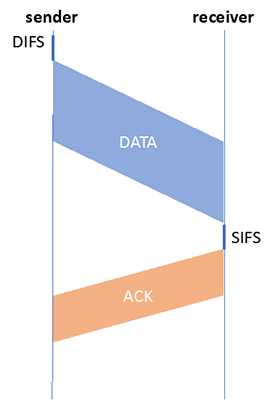
Figure 31 Data transmission in IEEE 802.11
In order to avoid collisions, allow sender to “reserve” channel rather than random access of data frames: avoid collisions of long data frames.
- Sender first transmits small request-to-send (RTS) packets to BS using CSMA
- RTSs may still collide with each other (but they’re short)
- BS broadcasts clear-to-send CTS in response to RTS
- CTS heard by all nodes
- Sender transmits data frame
- Other stations defer transmissions
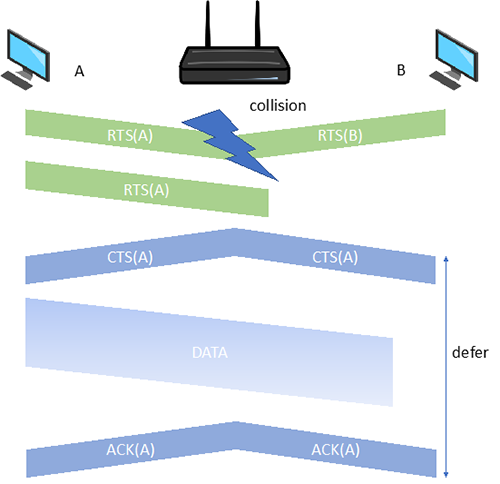
Figure 32 Data transmission in IEEE 802.11 using RTS and CTS





